基本计算器
题目
Implement a basic calculator to evaluate a simple expression string.
The expression string contains only non-negative integers, +, -, *, / operators and empty spaces . The integer division should truncate toward zero.
Example 1:
Input: "3+2*2"
Output: 7
Example 2:
Input: " 3/2 "
Output: 1
Example 3:
Input: " 3+5 / 2 "
Output: 5
Note:
- You may assume that the given expression is always valid.
- Do not use the
evalbuilt-in library function.
思路
字符串转整数
我们先看下字符串是如何转整数的,因为字符串表达式中间可能不是一位数,而是多位数,比如 1 + 23,其中 23 是一个两位数,读取的时候,先读到 2,要将其先转成整数存储下来,然后读到 3 的时候再将其放到个位:
s = '23'
num = 0
for c in s:
num = 10 * num + int(c)
print(num) # 23
加减
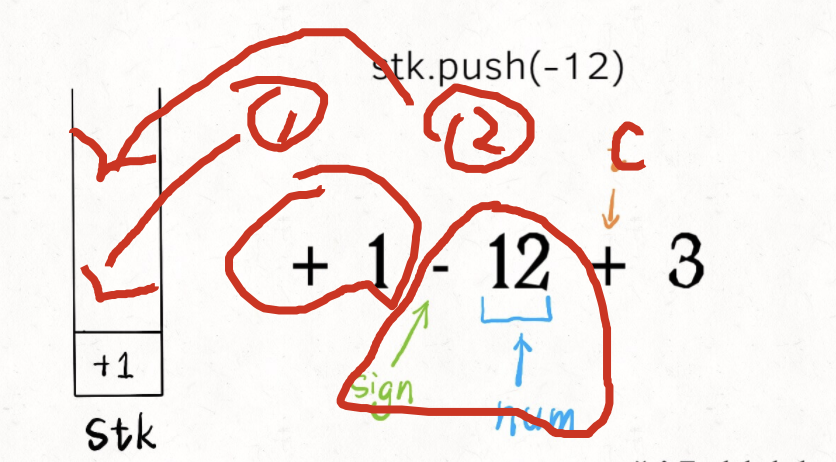
caution
不只是遇到新的符号会触发入栈,当遍历到了字符串的最后一个字符,也应该将前面的数字入栈,方便后续计算最终结果。
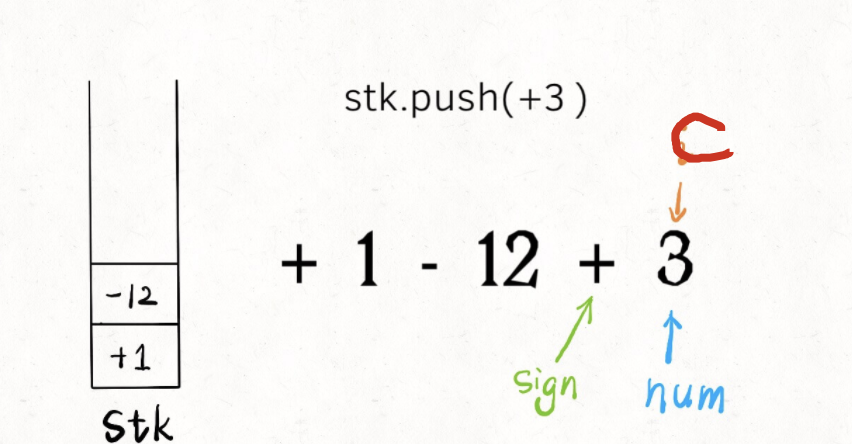
为了前后统一,可以在原始字符串后面直接加上 +:
for (let c of s + '+')
乘除
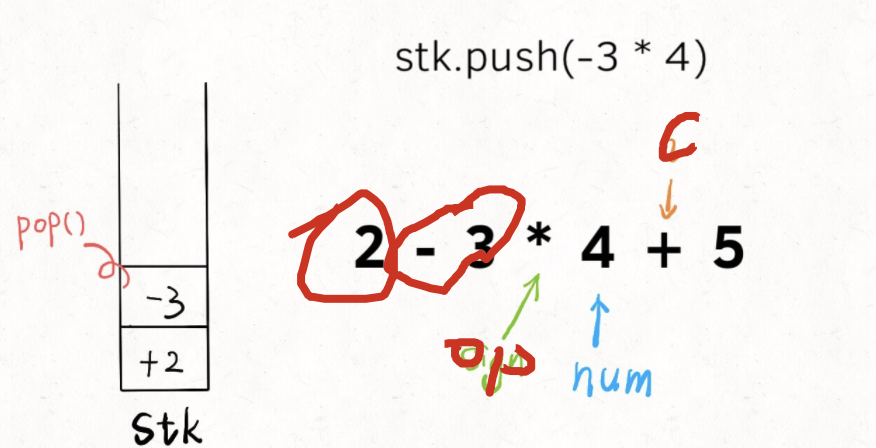
小结
遍历算式字符串,因为运算符有优先级,使用栈来存储每一次的运算结果。每次将运算符和其对应的算数计算后入栈,如果遇到高优先级的运算符,和栈顶元素运算完后再入栈。

代码实现
/**
* @param {string} s
* @return {number}
*/
var calculate = function (s) {
let num = 0;
let operator = '+';
let stack = [];
for (let c of s + '+') {
// '+'
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') {
num = num * 10 + +c;
continue;
}
if (c !== ' ') {
// 表示遇到下一个 operator
switch (
operator // operator 指的是上一个 operator,而不是现在的 c
) {
case '+':
stack.push(num);
break;
case '-':
stack.push(-num);
break;
case '*':
stack.push(stack.pop() * num);
break;
case '/':
stack.push(parseInt(stack.pop() / num));
break;
}
num = 0;
operator = c;
}
}
let res = 0;
while (stack.length > 0) {
res += stack.pop();
}
return res;
};
复杂度
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)