plugins 插件
Plugins
插件用于 bundle 文件的优化,资源管理和环境变量注入,作于用整个构建过程。插件可以看作是loaders功能的补充,对于loader无法完成的打包需求,可以考虑使用插件来实现。
常用的 Plugins
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| html-webpack-plugin | 创建html文件去承载输出的bundle |
| mini-css-extract-plugin | 将CSS从bundle文件里提取成一个独立的css文件 |
| optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin | 压缩 CSS 代码 |
| uglifyjs-webpack-plugin | 压缩js(从2.0.0 版 本开始不再支持 ES6 代码) |
| terser-webpack-plugin | 压缩js(Webpack4 已经内置该依赖包,支持压缩 ES6 代码的压缩) |
| clean-webpack-plugin | 每次构建后清除./dist目录 |
| friendly-errors-webpack-plugin | 优化命令行的构建日志提示信息 |
| speed-measure-webpack-plugin | 查看打包耗时、以及每个 Plugin 和 Loader 耗时 |
| webpack-bundle-analyzer | 可视化 Webpack 输出文件的体积 (业务组件、依赖第三方模块) |
| webpack-livereload-plugin | 开启监听模式时,代码更改自动刷新页面 |
| copy-webpack-plugin | 将文件或者文件夹拷贝到构建的输出目录 |
在webpack 3版本时,一般会使用CommonsChunkPlugin插件进行资源提取,但是在webpack 4版本中,推荐使用SplitChunksPlugin来代替CommonsChunkPlugin,而CommonsChunkPlugin已被删除。
在webpack 3.x的版本中提取CSS会使用ExtractTextWebpackPlugin,而在webpack 4该插件已经被MiniCssExtractPlugin替代。
Plugins 用法
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
output: {
filename: 'bundle.js'
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({template: './src/index.html'}) // 插件需要放到`plugins`数组中
]
};
Plugins overview
插件用于 bundle 文件的优化,资源管理和环境变量注入,作于用整个构建过程。插件可以看作是loaders功能的补充,对于loader无法完成的打包需求,可以考虑使用插件来实现。
- 常用的 Plugins
| 名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| html-webpack-plugin | 动态生成html文件去承载输出的bundle |
| mini-css-extract-plugin | 将CSS从bundle文件里提取成一个独立的css文件 |
| optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin | 压缩 CSS 代码 |
| uglifyjs-webpack-plugin | 压缩js(从2.0.0 版 本开始不再支持 ES6 代码) |
| terser-webpack-plugin | 压缩js(Webpack4 已经内置该依赖包,支持压缩 ES6 代码的压缩) |
| clean-webpack-plugin | 每次构建后清除./dist目录 |
| friendly-errors-webpack-plugin | 优化命令行的构建日志提示信息 |
| speed-measure-webpack-plugin | 查看打包耗时、以及每个 Plugin 和 Loader 耗时 |
| webpack-bundle-analyzer | 可视化 Webpack 输出文件的体积 (业务组件、依赖第三方模块) |
| webpack-livereload-plugin | 开启监听模式时,代码更改自动刷新页面 |
| copy-webpack-plugin | 将文件或者文件夹拷贝到构建的输出目录 |
为了更好的理解这些插件,可以点击下载我写的这个demo,本文中所有插件在 demo 中都有涉及,可以运行学习一下。
如果使用 uglifyjs-webpack-plugin 压缩 ES6 代码会报如下错误:

这时就需要使用 terser-webpack-plugin,直接引用即可,当然也可以自己再安装:
const TerserPlugin = require('terser-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
optimization: {
minimizer: [
new TerserPlugin({
cache: true,
parallel: true,
sourceMap: true, // Must be set to true if using source-maps in production
terserOptions: {
// https://github.com/webpack-contrib/terser-webpack-plugin#terseroptions
}
})
]
}
};
html-webpack-plugin
html-webpack-plugin 的主要功能是打包和压缩 HTML 文件,简化了 HTML 文件的创建,对于在文件名中包含每次会随着编译而发生变化哈希的 webpack bundle 尤其有用。当然你也可以不用这个插件直接创建一个静态 HTML 文件,如果需要动态改变内容的话在 webpack 里面通过 JS 来操作这个 HTML 文件,但这样比较麻烦,要想省事的话用 html-webpack-plugin 会简单很多。
html-webpack-plugin安装
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D html-webpack-plugin
yarn add --dev html-webpack-plugin
pnpm add -D html-webpack-plugin
webpack.config.json配置:
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require('html-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: path.join(__dirname, `src/split/index.html`), // 打包的html的文件路径
filename: 'split.html', // 打包后的文件名
chunks: ['split'], // 在打包后的html文件中引用的脚本
minify: {
html5: true, // 根据HTML5的规范来解析输入
collapseWhitespace: true, // 删除个节点之间的空白
minifyCSS: true, // 压缩style标签和style属性内的css
minifyJS: true, // 压缩script标签内的js代码
removeComments: false // 删除注释
}
})
]
};
通过上面的配置可以将index.html打包成只有一行的文件,文件名为split.html。通过chunks数组可以将打包好的某些bundle和chunk路径添加到.html的script标签的src属性上。minify各字段的具体含义和用法可以通过 html-minifier-terser 查询。
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
title | {String} | Webpack App | The title to use for the generated HTML document, can use <%= htmlWebpackPlugin.options.title %> in ejs file. |
filename | {String} | 'index.html' | The file to write the HTML to. Defaults to index.html. You can specify a subdirectory here too (eg: assets/admin.html) |
template | {String} | `` | webpack relative or absolute path to the template. By default it will use src/index.ejs if it exists. Please see the docs for details |
templateContent | {string\|Function\|false} | false | Can be used instead of template to provide an inline template - please read the Writing Your Own Templates section |
templateParameters | {Boolean\|Object\|Function} | false | Allows to overwrite the parameters used in the template - see example |
inject | {Boolean\|String} | true | true \|\| 'head' \|\| 'body' \|\| false Inject all assets into the given template or templateContent. When passing true or 'body' all javascript resources will be placed at the bottom of the body element. 'head' will place the scripts in the head element - see the inject:false example |
publicPath | {String\|'auto'} | 'auto' | The publicPath used for script and link tags |
scriptLoading | {'blocking'\|'defer'} | 'blocking' | Modern browsers support non blocking javascript loading ('defer') to improve the page startup performance. |
favicon | {String} | `` | Adds the given favicon path to the output HTML |
meta | {Object} | {} | Allows to inject meta-tags. E.g. meta: {viewport: 'width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no'} |
base | {Object\|String\|false} | false | Inject a base tag. E.g. base: "https://example.com/path/page.html |
minify | {Boolean\|Object} | true if mode is 'production', otherwise false | Controls if and in what ways the output should be minified. See minification below for more details. |
hash | {Boolean} | false | If true then append a unique webpack compilation hash to all included scripts and CSS files. This is useful for cache busting |
cache | {Boolean} | true | Emit the file only if it was changed |
showErrors | {Boolean} | true | Errors details will be written into the HTML page |
chunks | {?} | ? | Allows you to add only some chunks (e.g only the unit-test chunk) |
chunksSortMode | {String\|Function} | auto | Allows to control how chunks should be sorted before they are included to the HTML. Allowed values are 'none' \| 'auto' \| 'manual' \| {Function} |
excludeChunks | {Array.<string>} | `` | Allows you to skip some chunks (e.g don't add the unit-test chunk) |
xhtml | {Boolean} | false | If true render the link tags as self-closing (XHTML compliant) |
You can use ejs as well (by default, template will use src/index.ejs).
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: 'index.ejs', // customize the path of ejs file which is in root dir
alwaysWriteToDisk: true,
isProdEnv: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
}),
new HtmlWebpackHarddiskPlugin(),
<body>
<noscript> You need to enable JavaScript to run this app. </noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
<% if (htmlWebpackPlugin.options.isProdEnv) { %>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16.14.0/umd/react.production.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16.14.0/umd/react-dom.production.min.js"></script>
<% } %> <% if (!htmlWebpackPlugin.options.isProdEnv) { %>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16.14.0/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16.14.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<% } %>
</body>
Except above, you should set index.html as the default page as following:
app.get('*', (req, res) => {
// for example
res.sendFile(path.join(__dirname, 'dist', 'index.html'));
});
html-webpack-harddisk-plugin
You can use html-webpack-harddisk-plugin after HtmlWebpackPlugin. It keeps index.html at hard disk when using the webpack dev server or middleware(development env), so that you can simply doing this:
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
alwaysWriteToDisk: true
}),
new HtmlWebpackHarddiskPlugin()
];
mini-css-extract-plugin
mini-css-extract-plugin可以将样式代码从bundle文件里提取成一个独立的css文件。
需要注意的是mini-css-extract-plugin只可以用于未使用style-loader的production环境中。
- 安装
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D mini-css-extract-plugin
yarn add --dev mini-css-extract-plugin
pnpm add -D mini-css-extract-plugin
webpack.config.json配置:
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
module.exports = {
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/,
use: [MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader, 'css-loader']
}
]
},
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: '[name]_[contenthash:8].css' //
})
]
};
在使用该插件前同样也需要先引用mini-css-extract-plugin包,同时在css-loader前添加MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader,并且在plugins中实例化该插件。当CSS代码被打包成单独的文件后,会以 link 标签的形式插入到对应的.html文件中。
optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin
optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin用于优化压缩打包后的 CSS 文件,压缩代码默认会使用cssnano。
optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin安装
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin cssnano
yarn add --dev optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin cssnano
pnpm add -D optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin cssnano
webpack.config.json配置
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require('mini-css-extract-plugin');
const OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin = require('optimize-css-assets-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new MiniCssExtractPlugin({
filename: '[name]_[contenthash:8].css'
}),
new OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin({
assetNameRegExp: /\.css$/g, // 匹配css文件
cssProcessorOptions: {
preset: ['default', {discardComments: {removeAll: true}}] // 去除注释
}
})
]
};
当没有安装cssnano且cssProcessor: require('cssnano')没有设置时,插件会默认的引用cssnano,因此可以不在OptimizeCSSAssetsPlugin中配置cssProcessor。使用该配置打包后,.css文件代码会被压缩为一行。
clean-webpack-plugin
使用clean-webpack-plugin插件后,每次构建都会清除配置的输出目录。
clean-webpack-plugin安装
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D clean-webpack-plugin
yarn add --dev clean-webpack-plugin
pnpm add -D clean-webpack-plugin
webpack.config.json配置
const {CleanWebpackPlugin} = require('clean-webpack-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CleanWebpackPlugin() // 每次打包后,清理上次的dist目录
]
};
使用clean-webpack-plugin后,可以在构建前删除输出目录,相比于使用rm -rf dist && npm run build更灵活方便。
friendly-errors-webpack-plugin
friendly-errors-webpack-plugin可以更直观的定位webpack错误,为开发人员提供更好的体验。
使用friendly-errors-webpack-plugin后,每次打包都会有一个标签提示,标签提示一共分为以下三种:
DONE表示打包成功,并会返回打包用时。WARNING也代表打包成功,但是打包文件的依赖可能存在不合理的地方,例如当导入自定义的字体过大时,会WARNING预警。ERROR则代表打包失败,打包失败后会在控制台指出错误的位置,这一点在不安装该插件时是没有的。
使用该插件这三种情况可以通过 npm 仓库中friendly-errors-webpack-plugin的 demo 进行查看。
friendly-errors-webpack-plugin安装
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D friendly-errors-webpack-plugin
yarn add --dev friendly-errors-webpack-plugin
pnpm add -D friendly-errors-webpack-plugin
webpack.config.json配置
const FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin = require('friendly-errors-webpack-plugin');
const webpackConfig = {
plugins: [new FriendlyErrorsWebpackPlugin()]
};
为了更好的理解该插件可以下载webpack-demo/plugins执行以下,运行效果如下所示:

speed-measure-webpack-plugin
使用 speed-measure-webpack-plugin 可以测量打包耗时、以及每个 Plugin 和 Loader 的耗时。
- 安装
speed-measure-webpack-plugin
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D speed-measure-webpack-plugin
yarn add --dev speed-measure-webpack-plugin
pnpm add -D speed-measure-webpack-plugin
webpack.config.json配置
Change your webpack config from
module.exports = {
// ...
plugins: [new MyPlugin(), new MyOtherPlugin()]
// ...
};
to
const SpeedMeasurePlugin = require("speed-measure-webpack-plugin");
const smp = new SpeedMeasurePlugin();
// ...
module.exports = smp.wrap({
// ...
plugins: [
new MyPlugin(),
new MyOtherPlugin()F
]
// ...
})
打包后会在控制台打印出各 Plugin 和 Loader 的耗时,如下图所示:

通过打包的结果可以更方便找出需要优化的部分,加快构建速度。
webpack-bundle-analyzer
使用webpack-bundle-analyzer,可以用交互式可缩放树图可视化 webpack 输出文件的大小。
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D webpack-bundle-analyzer
yarn add --dev webpack-bundle-analyzer
pnpm add -D webpack-bundle-analyzer
webpack.config.json配置
const {BundleAnalyzerPlugin} = require('webpack-bundle-analyzer');
module.exports = {
plugins: [new BundleAnalyzerPlugin()]
};
打包后的交互式可缩放树图如下图所示:

通过使用该模块可以帮助我们:
- 打包出的文件中都包含了什么,以及模块之间的依赖关系
- 每个文件的大小在总体中的占比,找出较大的文件。
- 是否有重复的依赖项。
- 每个文件的压缩后的大小。
webpack-livereload-plugin
在 webpack 为监听状态时,实现代码的热加载,与之类似的模块还有webpack-dev-server,这些内容将在后续代码热更新部分详细提及。
- 安装
webpack-livereload-plugin
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install --save-dev webpack-livereload-plugin
yarn add --dev webpack-livereload-plugin
pnpm add --save-dev webpack-livereload-plugin
webpack.config.json配置
var LiveReloadPlugin = require('webpack-livereload-plugin');
module.exports = {
plugins: [new LiveReloadPlugin(options)]
};
options 为用户自定义字段,可以根据自己的需求配置相应字段,各字段含义可以通过webpack-livereload-plugin文档查看。
在控制台使用npm run watch命令监听文件的变化,热加载打包的效果如下图所示:
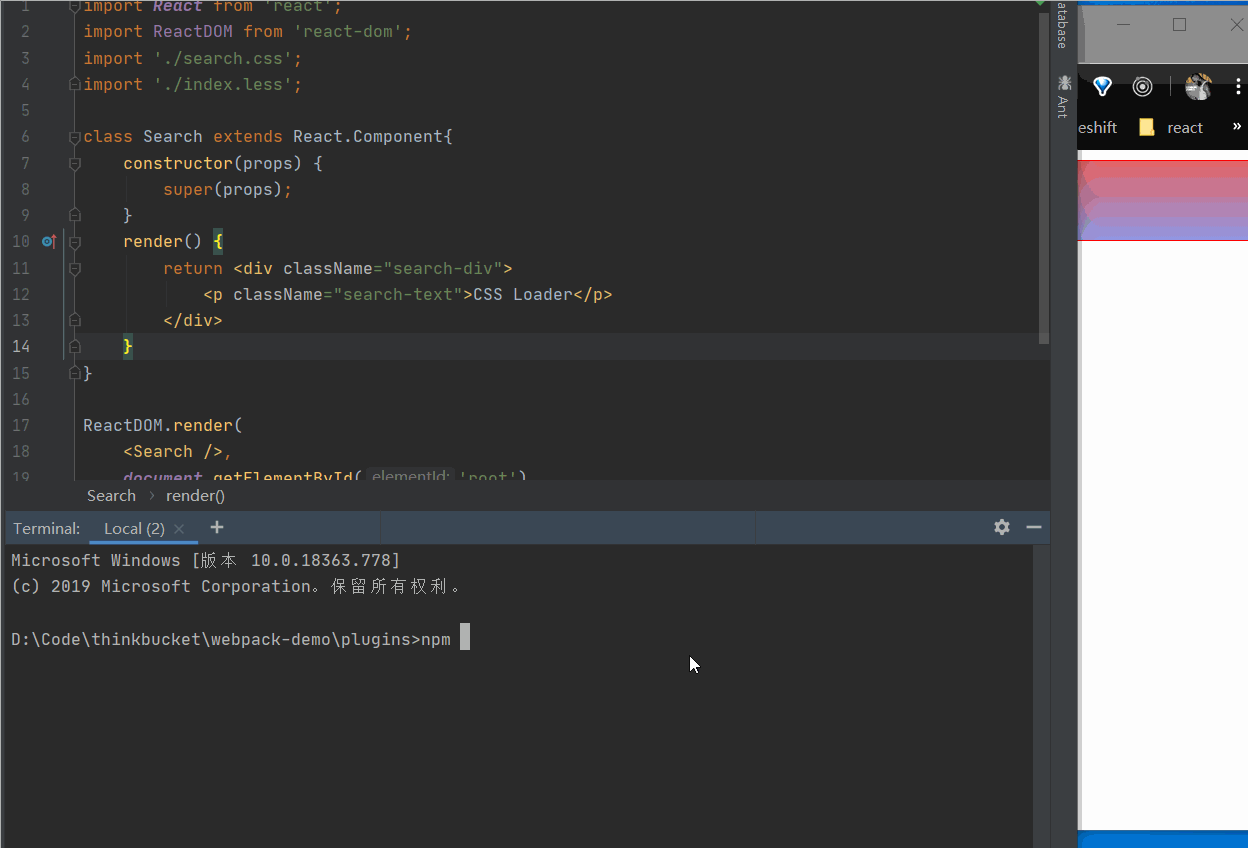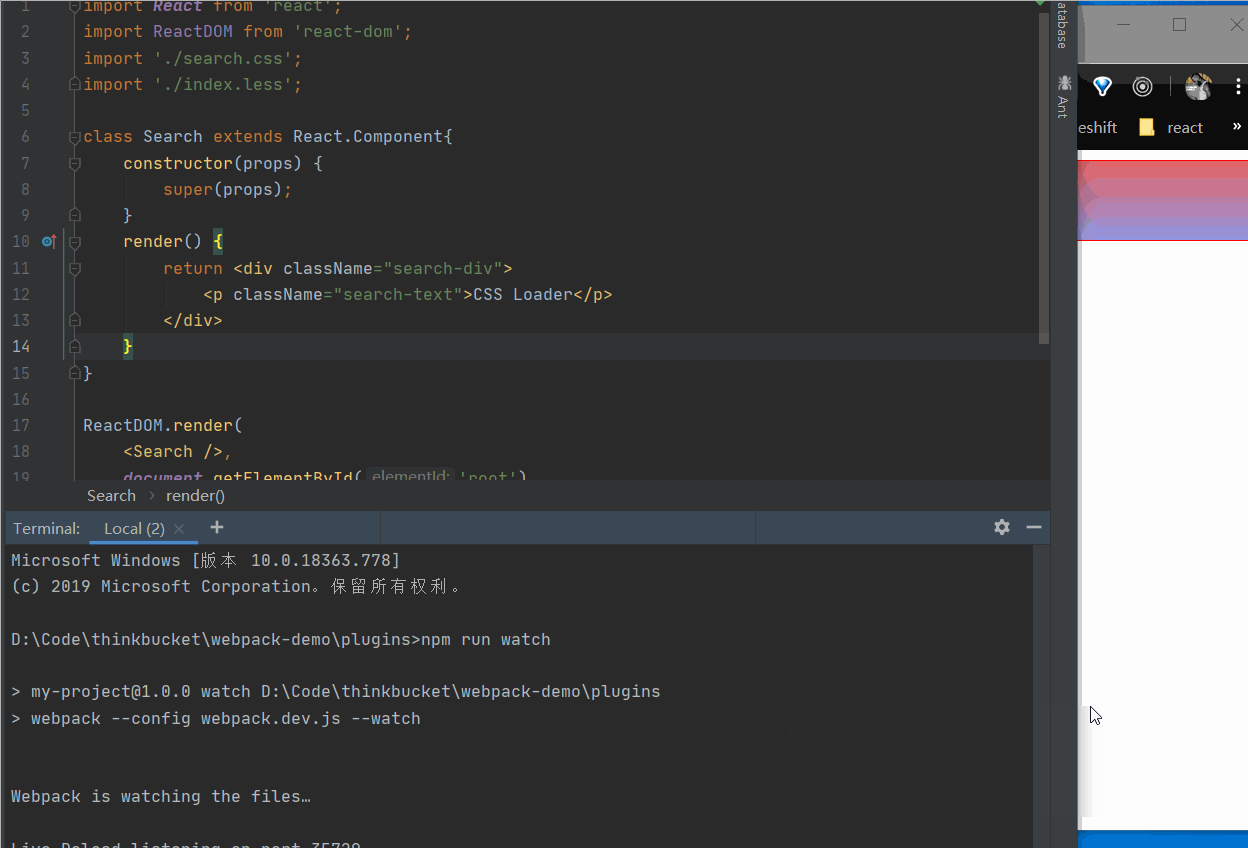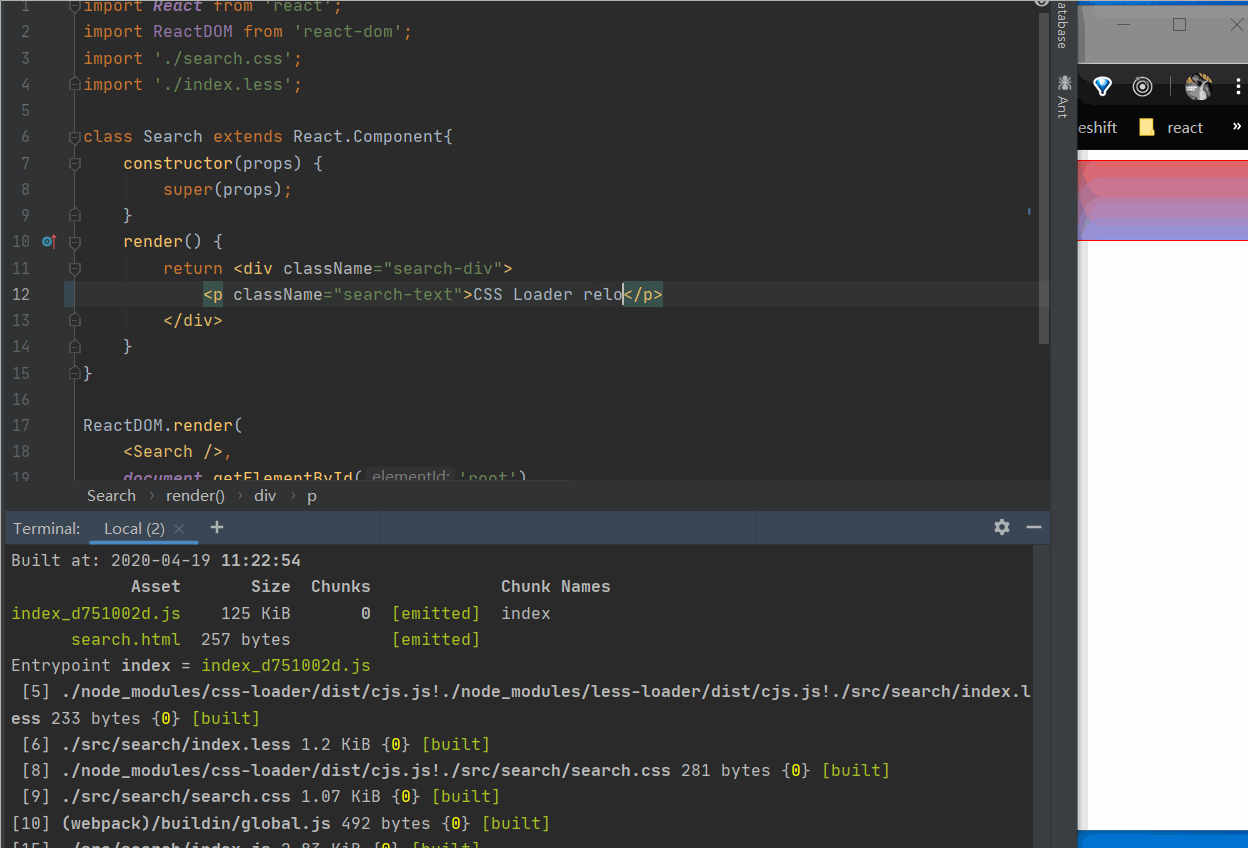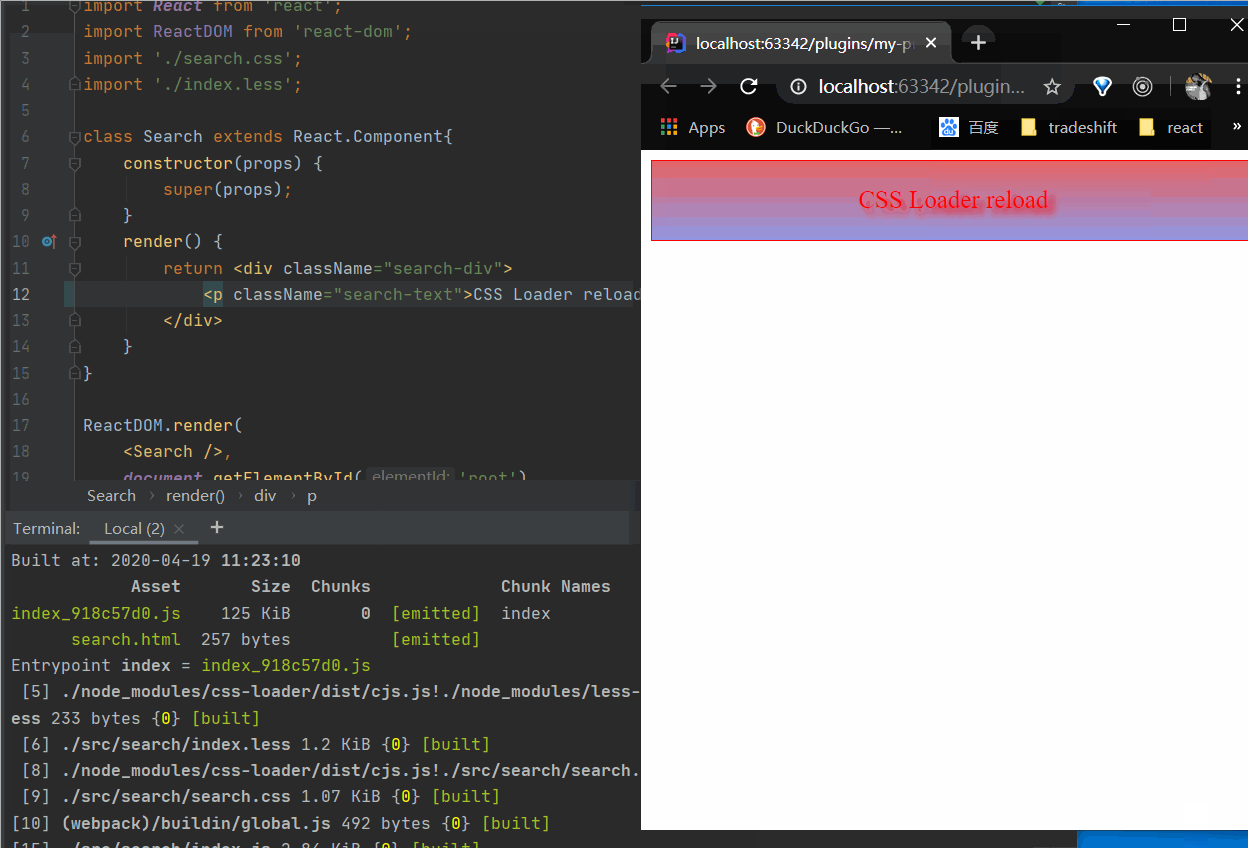
copy-webpack-plugin
使用copy-webpack-plugin可以将单个文件或整个目录复制到构建目录。
- 安装
copy-webpack-plugin
- npm
- Yarn
- pnpm
npm install -D copy-webpack-plugin
yarn add --dev copy-webpack-plugin
pnpm add -D copy-webpack-plugin
webpack.config.json配置
const CopyWebpackPlugin = require('copy-webpack-plugin');
const config = {
plugins: [new CopyWebpackPlugin([...patterns], options)]
};
实例化CopyWebpackPlugin时,可以传入两个参数patterns和options,其中patterns存放着要拷贝的文件路径和输出路径,例如:
module.exports = {
plugins: [
new CopyWebpackPlugin(
[
{
from: __dirname + '/src/copy-test', // 将/src/copy-test目录下的文件拷贝到dest目录下
to: __dirname + '/dist'
}
],
{copyUnmodified: true}
)
]
};
options表示其它配置,一般可能会设置为copyUnmodified属性。使用--watch或webpack-dev-server时,如果copyUnmodified默认值为false表示只复制修改的文件。如果设置为true,代表只要有文件修改,所有文件都会被复制一遍。
与CopyWebpackPlugin相关的更多配置,可以参考CopyWebpackPlugin
使用上述配置的打包结果如下所示:
